Abstract: The following paper explains the concept of dependent origination and its place in Buddhist Dharma (teaching).Dependent origination is then described as a heuristic and discussed in relation to James Lovelock’s GAIA hypothesis, the solar system, the economic system, the social environment, event phenomena and entrepreneurial opportunity, consciousness and self concept, and the ethical standpoint.
1. Introduction
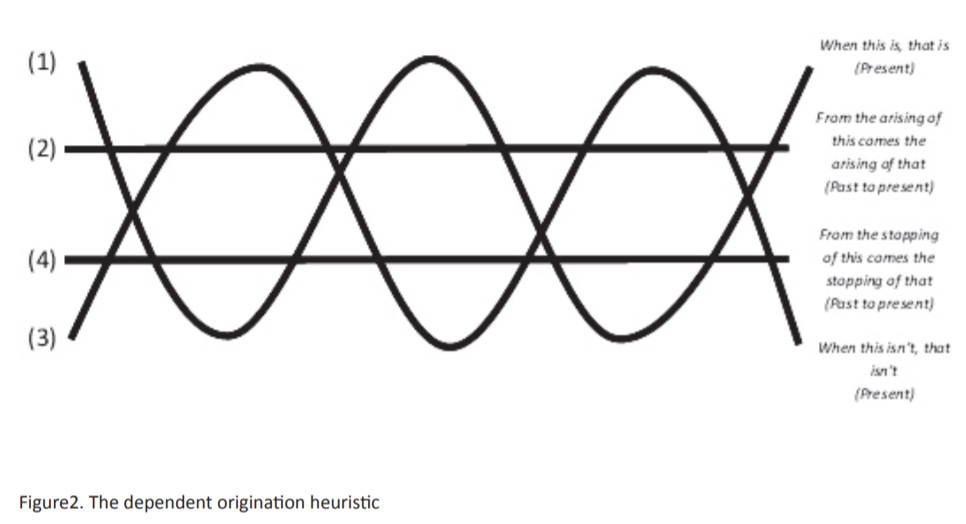
When there is this, that is
With the arising of this, that arises
When this is not, neither is that
With the cessation of this, that ceases
--Law of Universal Nature (1)
The concept of dependent origination (paticcasamuppada) (2) was developed by the spiritual teacher Siddhartha Gautama who became known as the Buddha upon enlightenment. (3) The Buddha used the concept to explain a causal relationship between worldly experiences and suffering or dukkha of people through everyday life phenomenon. The Buddha's straight forward teaching was in stark contrast to the practices of society in India at the time where people worshipped 'sacred' objects, 'supernatural' beings, and performed rites and rituals based on superstitious beliefs. Buddha's teachings did not contain the mystical or concern itself with metaphysical issues, although he stretched the meanings that people already knew to create new meanings. (4) Others superimposed esoteric teachings after his death. (5) However the presence of the esoteric is part of the poetry of teachings that assists in conveying meaning within the paradigm of human consciousness at the time. (6)
The Buddha's revelations came at a time when his contemporaries were influenced by astronomy, where the universe was seen and explained as a linear and regular entity, with consciousness separated from the universe and the universe separated from consciousness. (7) This mechanistic view of the world was expounded upon by Descartes, Newton, Weber and later Frederick Taylor in the management arena with influence lasting well into the 20th century. Since the end of the European renaissance the metaphor of science has been that of the machine with the universe being described as 'grand clockwork ' where the planets spin around the sun in a predictable fashion, described by the precision of mathematics. Science reduced everything to the smallest part in the belief that if one understood the parts one would understand the whole system. Reductionism is the standard of science. (8) This thinking still prevails through the means of how we live and organize ourselves, where organizational charts, job descriptions, policies, strategies, budgets, and operational plans are utilized as a means to control of the organization and environment like a machine. This has been adequate where a stable equilibrium exists, but this itself is only a myth. The predominating theories were observer based where predictable order, stability, separation from the individual, and grounded fixedness' are the major characteristics.
In contrast, dependent origination presented an alternative view to the world to what Descartes and company espoused. Dependent origination postulated a co-evolutionary interrelated world based on co-dependency, built upon dynamic cause and effect to create aggregate conditions, rather than the accepted 'Newtonian order ' of existence.
Although the philosophy of dependent origination, which is considered 'the heart ' of Buddhism, (9) can be applied widely, the Buddha restricted his application of the principles to the development of human nature and explanation of suffering. On metaphysical and matters of the hereafter, he was silent, thus the concepts are very vague for application for other domains. Nevertheless, the concept of dependent origination can be closely aligned with many aspects of quantum mechanics, (10) systems (11) and chaos theory, (12) Darwinian natural selection extrapolated to a cosmic scale, (13) Dawkins views about evolutionary biology, (14) the Gaia hypothesis, (15) and cognitive science. (16) The concept of dependent origination distinguishes Buddhism from religion (17) as according to dependent origination a creator is not necessary in forming the cosmos which has been postulated to evolve through causal dependence in a similar view taken by Hawking and Mlodinow. (18)
2. The Doctrine of Dependent Origination
The general principle of dependent origination concerns the fundamental structure of nature and how the elements within it interrelate. The doctrine of dependent origination looks upon the universe as a continuous succession of action, reaction, and effect within a state of dynamic flux and transformation. Max Brown postulated that the occurrence of entity "A" relies upon the occurrence of entity "B", i.e., "B" is the cause of "A". This implies antecedence where causes must precede or at least simultaneously exist for something else to exist. These phenomena must be spatially connected by a chain of immediate things in conduit. (19) However this is abandoned by dependent origination where mutual arising with entities co-depending upon each other for existence. Dependent origination is not a sequential linear process; it is a cycle with no beginning and no end.
Charles Darwin in the last paragraph of The Origin of Species wrote, "It is interesting to contemplate a tangled bank, clothed with many plants of many kinds, with birds singing on the bushes, with various insects flitting about, and with worms crawling through the damp earth, and to reflect that these elaborately constructed forms, so different from each other, and dependent upon each other in so complex a manner, have all been produced by laws acting around us." (20)
This gives us a perspective of his sense of wonderment about the complexity (21) and interrelationships within the biological system of life and evolution that the concept of dependent origination postulates. Thus only through interrelatedness can we see meaning:
Paper without a tree
A tree without soil
Soil without water
Water without clouds
Clouds without an atmosphere
An atmosphere without oceans.
This according to Winnicott is also relevant to human relationships, the family and the outside world: (22)
A child and a parent
A parent and a partner
Partners and family
Family and friends
Friends and humanity
Humanity and nature.
Everything in the realms of nature and humanity are dependent upon each other for existence. Things only exist through relatedness. (23) We can only exist through relatedness. Nothing can exist in isolation as it all depends upon numerous determinants which are all interrelated. If one doesn't exist then the rest can't exist. This continually changes, therefore entities change all the time.
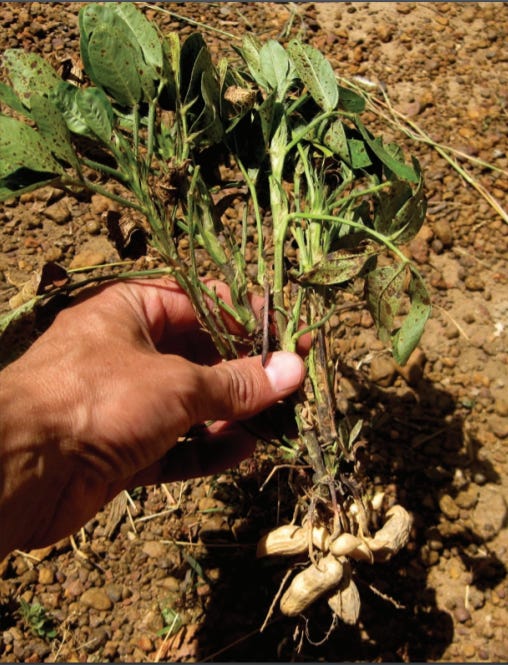
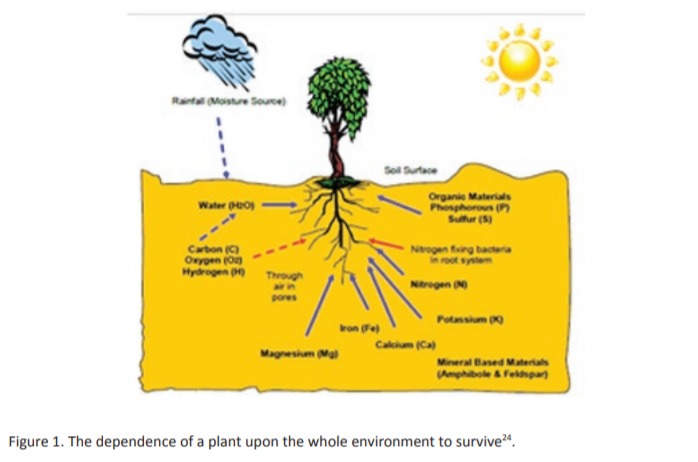
This can be clearly demonstrated with a plant where the plant relies upon the soil as a medium, minerals and nutrients to grow, moisture as carrier for the nutrients and a building block for cellular structures and the sun to enable photosynthesis for the building to occur. Without any of these, the plant cannot exist. The determinants that enable a plant to grow do not influence the plant in any sequential order of time. They must exist together, interdependent of each other. The plant contributes to maintaining the system through the shedding of leaves and other foliage, which decays, adding to the humus and trace minerals in the soil. In theory for anything to exist in isolation, it must be self-sustaining and stable. However within the laws of nature that is impossible, thus as a consequence everything is only transient with no intrinsic properties of its own. All entities are created and sustained through interrelationship. There is no beginning or end as the question of what came first cannot be answered: "the seed or the plant, or the chicken or the egg?"
There is no such thing as chance. Every event is a result of the consequences of previous events, cumulating as multiple influences upon what is. Therefore the notion of chance depends upon preconditions. As nothing exists in isolation, everything depends upon pre-determinants that are not sequential or required to arise in any particular order. This is in great contrast to the classical paradigm where the universe was deemed to be predictable like billiard balls rolling upon a table. Metaphorically quantum behavior is also attuned to human behavior which is much less predictable and impossible to measure through mathematics; where only probability can be predicted through heuristics.
Dependent origination as a universal heuristic would look something like figure 2. The lines represent and interplay of two causal factors, one linear and the other synchronic that contribute to a non-linear pattern. Lines (2) and (4) are linear and connect past events overtime to the present and ground the future. Lines (1) and (3) are synchronic and connect objects and events to the present moment. These two basic principles intersect representing that all events are influenced by the two sets of conditions. Structurally this divides a system into parts, connecting the past, present and future together. The past and present circumstances determine the present which creates consequences for the future. However don't confuse time itself as a determinant, as time is itself a 'manmade ' invention, a construct.25 Only a cyclic time exists, relative to arising and cessation exists. Time itself does not directly influence events. Time can only be used to explain what happens within its relativity metaphor framework.
Every event takes place in a context determined by the combined influence of past events (what was) and present circumstances. Every event has repercussions in the present with reverberations extending into the future (what will be). The strength of the influence will depend upon the intensity of the event. Sometimes events reverberate and amplify an effect and sometimes events may suppress an event. (26) However, this is not the result of a chain of causes leading to effects strung over time. Any event may be affected by a past event and present circumstances which may lead to unexpected feedback loops during the causal process. (27) Due to this possibility of any event happening at any time, the causation or arising process is extremely fluid and complex. (28) The Pali explains the phenomena using the metaphor of water rather than the wheel of samsara, thus metaphors such as ebb and flow are much more suitable than "sequencity".
If everything existed in linear relationships, everything would be totally predictable and deterministic and the future would be unable to change from the present and past. If everything was totally in synchronic relationships there would be no relationships from on period to another and all events would be totally random and completely unpredictable. Everything would just break down and change without reason and connection. The two modes work in concurrence where past events and present circumstances create a potential, but not completely determined path.
Critical to the continuality of the processes of dependent origination is feedback. Feedback is one of the energies (along with momentum) that enable the system to operate continuously as a self organizing system. To understand how particular feedback occurs is to understand the manifestations of dependent origination. It is this feedback which defines interdependency. However this understanding may be beyond our cognitive abilities and is thus one of the challenges for mankind to overcome in the future.29
Closed feedback loops are responsible for linearity of the system and open feedback loops are responsible for non-linearity of the system. Closed feedback loops influence quantitative rates within a system, such as a thermostat regulating temperature in a room. Open feedback systems are more dynamic and allow for changes in the state of a system, like the change in direction of wind within a weather system that brings a change in the state of weather.
Simple closed loop feedback systems can be responsible for counterintuitive behavior. (30) For example, we usually over correct heater thermostat systems which lead to oscillations in room temperature until we find a stable range. This is very similar in a free market pricing mechanism in economics where an increase in price leads to the entry of new producers until supply outstrips demand and the price decreases to a level where producers leave the industry, leading to supply shortages and increases in prices once again, in a continuous cycle.
Open systems tend to operate with multi-loop non-linear feedback systems where many variables provide for unpredictable results. It is the interaction of counter-reactive feedback loops that provide the unpredictability and chaos within the system. Mathematical formulas are centered on linearity and cannot predict the outcome of a system that is both emergent and a self organizing system. As the number of feedback loops increase the complexity of the system increases exponentially. (31)
If one traces back the stream of events, no root causes can be found for anything. Events are an emergence, a natural evolution where there is a mutually arising. (32) Open systems are just too complex to determine any single cause, and selecting single causes to explain phenomena would just delude reality. Consequently there is no beginning and end, just a continuous flow of events.
The doctrine of dependent origination applies to all things and subsequently all things are influenced by cause and effect, Kammaniyama the law of karma determines future behavior. All events and phenomena produce karma. Karma is the 'potential' generated by 'cause and effect' or the interrelationships between dynamic entities. (33) Karma can have a positive or negative consequence upon the future. Karma being a 'potential' (34) is what keeps the universe transient across time dimensions. To some degree karma actually provides the substance to time, as without karma there would be no change in the universe and thus no time. (35) Karma is regularly mistaken for something psychic that acts upon the soul, more attuned to the romantic narrative of a humanized religious version of Buddhism, (36) or the mythology of reincarnation based on past deeds done upon the Earth. Other misinterpretations describe karma as a form of fate.
3. The Application of Dependent Origination in Buddhism
In Buddhism dependent origination or paticcasamuppada is applied to the arising and cessation of human suffering. (37) Paticcasamuppada explains how suffering arises and how suffering ceases as a matter of natural interdependence, i.e., everything arises, exists, and passes away in a transitory manner. (38) According to the principle of dependent origination all human thoughts and feelings are grounded in ignorance which deludes one to a false sense of self which we call "I' or "me", when in fact there is really no self in existence, just the illusion of a self based on emotions. Only a deluded self can be part of the cause and effect that occurs within dependent origination as karma, where all intentions, thoughts, feelings, and actions have consequences.
The teaching of paticcasamuppada attempts to clarify the events of nature as they actually occur in order to highlight the causes and correct them. Dependent origination occurs within the context of flowing through a number of states of ignorance and types of attachment. Buddhist teaching of paticcasamuppada covers three lifetimes which implies the existence of something that passes from one lifetime to the next. However this is only metaphorical as it is contrary to Buddha's teachings. (39) There are twelve dependent origination links which resemble a person's thought processes.
Ignorance of the truth as things really are and being deluded by nominal realities is the first of twelve situations in dependent origination. Ignorance builds up over time and become ingrained within our deepest inner assumptions as fears and anxieties, such as the fear of mortality. Ignorance can emerge into a psychotic state where basic 'good' or 'bad' are difficult for a person to determine. (40) With this basic ingrained ignorance, intention and thought is influenced.
This is a prerequisite to the second link karma where our continued greed, envy, anger, becomes the basis of our personality, beliefs, and habits. Our thoughts, speech and actions create karma. Karma is the law of cause and effect in relation to our mind, speech and actions, i.e., causation. Human ignorance and corresponding actions are a past cause of karma and current action creates new karma. New karma is continually generated through our 'mindstream' and is maintained within us like a storage bank. Karma can be good or bad depending upon the nature of our actions. Our stored karma determines how we perceive and respond to stimuli in the world. This becomes the motivating force behind action and is thus important to the concept of dependent origination on a personal and social level.
The third link, our consciousness (41) is conditioned into a basic mind-state where we have a tendency to see what we want to see. Due to the large number of stimuli within the world we live within, attention focuses our mind on specific objects in a similar way a filter takes out what is not wanted. There are many stimuli and corresponding mental factors operating at once, however the mind is unable to process them simultaneously. In this situation only data from one sense can be processed at any one time. This means for example if driving a car and speaking on a mobile phone at the same time, stimuli from outside the car and from the phone can only be processed sequentially, meaning we are experiencing an illusion that both are operating together. (42) We do this through our body and mind, the forth link referring to our five forms that constitute a person, namely the physical being including sight, hearing, taste, smell, and tactile feeling, sensation and feelings, i.e., contact between the body and objects, perception and ideas, i.e., our ability to recognize objects and ideas, mental labeling and acts, and basic consciousness. (43) Through our senses, the fifth link, we see, hear, smell, taste, or feel an object without making any identification or giving any label to it.
Once our senses make contact, the sixth link, raw data is collected and must be identified through the process of discernment where the object's characteristics are matched against templates in the mind (memory) where a focused awareness and coordination of the senses with our mental impressions through our perceptions occurs, the seventh link. (44) This gives rise to volitional impulses that guide of focus and concentration and influence the value and meaning on the objects we see. (45) Once the object is identified, feelings of desire or repulsion arise. These feelings then develop into a like or dislike for the object which trigger feelings of desire or repulsion. Desire or repulsion varies in intensity from a mild to a strong attraction or repulsion for the object. It is the feeling which gives value to any object by a person. This is attachment which is the eighth link.
Feelings are generated from our natural condition, mental disposition, personality, and training. Our natural condition is the intuitive tendency we feel towards any object we come into contact with. There will be a natural tendency to go towards or away from the object. In addition our mental disposition is affected by our moods and can be influenced by altered mind states like intoxication. Our life experience, environment, and cultural influences all contribute to the development of our personality and preferences that influence how we act. Consequently we look at things in a prejudiced light, in a 'good' or 'bad' light, stereotyping objects and people. (46) Our actions are more related to our impulses rather than the actual reality. (47) This is a confused and ignorant consciousness where understanding the concept of our non-permanence is impossible. If consciousness cannot be transformed from ignorance to enlightenment, then the person will continue to endure suffering.
The process of attachment begins at birth where we are quickly dependent on our mother and create likes and dislikes for things. As these emotions are strong, the majority of people are incapable of withdrawing from these attachments in life. (48) The thought processes that lead to attachment are important to how we identify our own sense of self and being. This is agreed upon by many psychoanalysts, including Freud, who saw traits like anger, aggressiveness, craving, hatred, and lust making a large contribution to how we see ourselves. (49) Attachment also gives objects, people and events value and meaning that may differ from the actual reality. It becomes the "lens" through which the environment is experienced and interpreted. (50)
There are different forms of attachment. (51) Sensual attachment occurs when we like possessing objects that we are enchanted with. These objects include colors, shapes, sounds, odors, flavors, other objects of desire, images (whether real or imaginary) of the past, present and future that are in the mind. Sensual attachment can lead to feelings of envy, anger, arrogance, hate, and can even lead to acts of murder and suicide. Everything a human does has some origin in sensual attachment and it is the power that drives people to study, work and earn money in the search for pleasure. Because of the desire to feel good, one can become a slave for all the trappings of status, power, wealth, and comforts that it brings, even though it forces one to agree all the time. Such a relationship brings out arrogance, ostentation and blind attachment. The desire to go to heaven preached in most religion also has its roots in sensuality. Sensuality is the primary form of attachment.
To have one's own opinions is very natural. However when ideas and opinions become cemented into a person's mind and they cling to them, this becomes attachment. Many of these opinions are bound up in customs, professions, religions, traditions and rituals and our perceptions become dogma based upon the beliefs a person subscribes to. (52) They become stubborn convictions which cannot be changed due to the cement of long held traditions, professional practices and/or beliefs. The clinging to views and opinions is based on original ignorance, where existence becomes very mechanical with programmed type responses. If we see wrong we rarely admit it, often leading to anger and even violence or war, where naive doctrines are held. When we become attached to our sheltered culture, imagination and perceptions, the potential for progress and development is hindered. When things are considered sacred and cannot be changed under any circumstances, i.e., beliefs about 'artifacts' like qualifications, 'magical processes' like strategic planning and 'secret procedures' like employee selection, rationality is distorted and becomes a barrier to change.
Finally, one can be attached to the belief of the idea of 'self' or 'I'. This is also a common occurring form of attachment and like attachment to opinion, is very hard to detect. The paradigm of 'me and mine' is based on our primal instincts to hunt and gather, procreate and protect, etc. We also tend to see our existence as eternal and fear the concept of death. This form of attachment eliminates any beliefs in transience where the person unconsciously develops delusions of permanence and solidity. This creates the fear of loss and desire to defend and protect both time and space as something needing to be held onto. Freud also saw the importance of the sense of loss to a person - love, object or experience, and saw that loss (and potential loss) can lead to manifestations of depression and anxiety. (53) This most often leads to the search for pleasure seeking experiences to avoid further pain and suffering.
Another consequence of the 'me and mine' paradigm is the development of aversion. When something threatens our self image, aversion steps in to maintain our self notion of permanence. Aversion may range from simple avoidance of the issue, to dissatisfaction, frustration or intense anger. The source of all these symptoms is our ignorance of our self at the unconscious level where the mind exaggerates the negative parts of our self image. (54) Attachment can also feel good as it may be covered in love, i.e., slave of a person, or anger with oneself may be covered with hate for something or someone external to oneself. These symptoms develop into a number of defense mechanisms.
Craving is the ninth link, which is more intense form of attachment. People are not content with what they have and desire to seek pleasure and avoid pain, even at the cost of harm to others. Craving motivates one to capture and control these sources of pleasure. This becomes an aversion to other things. As desire becomes stronger it develops into clinging, a fixed position is adopted towards things. This may refer towards things, processes, practices, models, the belief in oneself, etc. Therefore life situations are evaluated and appraised from these standpoints, i.e., a person's approach or self view. The removal of loss of pleasurable things can lead to grief. This is intensely selfish and leads to bad karma which traps one in a state of delusion.
Clinging leads to becoming where one exists within a set of conditions of life states both at the physical and mental level, which influences patterns of behavior, character traits and aspirations. This affects life situations where the person is influenced about what they think and how they behave from their form of becoming. Their thinking and emotions are patterned within their belief systems and aspirations, values, and according to what behavior has worked in the past. Most people live within this deeply conditioned type of life. Their actions produce karma that results in long term consequences and also influences their own deep character traits. At this stage of life things seem permanent and a distinct sense of self exists identifying with a life situation, i.e., feelings of one as an owner, a success, a failure, and so on. Wisdom doesn't exist as one is programmed by their deep set beliefs and traits. The 'I' is strong and superior and this identity is staunchly defended. Arrogance emerges with a sense of authority
However with this becoming comes the opportunity for another birth, the tenth link. A person with a life of craving through ignorance will be doomed to be re-birthed within the cycle of samsara. (55) However upon reflection, one may realize their state of delusion and rebirth themselves with all sorts of new possibilities. (56) According to Erikson, a person goes through a number of stages during their life where their identity, achievements and self worth are questioned. (57) Thus a person may find emptiness in their life that leads to evaluation and the hope of change. Within this period of questioning there may be a change in existing relationships, the taking up of new activities, or the commencement of self employment with a sense of spiritual guidance influencing the future path. This phenomenon is not restricted to midlife. Situational changes may influence people to react and respond to newly perceived circumstances. (58) Crisis can occur anytime during life, leading to new revelations, and needs to re-evaluate one's life achievements. (59) If no change occurs then one is doomed to following the same existence which is the eleventh link. Birth refers to the 'birth of the moment ' rather than a physical birth of a new life.
The final link death is a reminder that nothing is permanent and all humans face the ultimate truth of dependent origination. Life entails the experience of decline within it. These include the imminent degeneration of that state the experience of adversity and ruin within it. The inevitability of decline and dissolution together with the constant anxiety and effort to protect oneself from the inevitability of mortality causes sorrow, pain, grief, despair and suffering. One day the self will be deprived of its position which may bring neurotic thinking and behavior and fear of death. One also faces disappointments with what was not achieved. Those with a sense of success are dependent on external factors such as fame, praise, attainment, or special privileges, or recognition, etc. One occupies space with boundaries and develops this dualism of self and non-self.
Thus the delusion of the self is the cause of all grief in peoples' lives. The existence of people as entities is the wrong view. (60) The wrong view is where people are deluded into believing that we are a soul. In fact the soul is only a paticca-samuppanna-dharma which arises in response to the natural law, i.e., the result of events which dependently arise upon other things such as contact with objects that bring feelings that lead to greed and craving that leads to the delusion that one exists. Any soul cannot exist in isolation, it is the product of emotions and the conditions that give rise to emotions, which enables the mind/body to think, speak, and act.
Thus belief in a person as an entity is the wrong view in Buddhism. It is only the deluded sense of self that is part of cause and effect or karma, where all thoughts, feelings and intentions have consequences. Through mental conditioning developed by training, one can change their programmed response to objects. This can be seen when learning to drive a car. When just learning we need to concentrate on every action taken, but once driving is conditioned within the mind, one does not require the same concentration and actions taken appear to happen intuitively and naturally. In Buddhist practice paticcasamuppada is concerned about developing wisdom to enable a person to override the emotions that arise when the senses contact stimuli in the environment. When ignorance clouds the mind suffering arises which generates into an existence of permanence in attitude, bias and belief. However when mindfulness and wisdom govern the senses, suffering will cease. Becoming free of the wrong view and extinguishing suffering is the principle objective of Buddhism. (61) Freedom from suffering is a form of selflessness, where interpretation differs between different schools of thought. (62) This path can be practiced as cause and effect exists in the 'here and now' rather than in some past fate determined situation. If the cause of suffering is from a past life,63 then one cannot become free from suffering which is contrary to Buddhist teaching.
Dependent origination is a non-literal philosophy, open to wide interpretable meanings. (64) The rest of this paper will consider dependent origination within various types of environments, event phenomena (opportunity), consciousness and self concept, and ethics.
4. Applications of Dependent Origination
Siddhartha Gautama once was reported to say that "the whole world, how it arises and how it ceases is to be discovered in the actuality of this fathom-long body." (65) All phenomena are complex and as a consequence any analysis through reasoning is beyond our cognitive capabilities. Thus we can only derive partial meaning of any phenomena, as all phenomena have multiple layers of meaning, of which we are usually only able to pick out the other layers, leaving the inner and middle layers unexamined.
Reductionist tools like mathematics and geometry have great difficulty in explaining everyday occurrences like the operation of a steam valve, a tennis game, riding a bicycle, and catching a ball as there is the element of chaos (not to be confused with crisis) and unpredictability in any phenomenon. One can develop complex wave equations but never really know exactly what is going to happen. Reductionism relies upon linear perfectionism which doesn't exist. Even the earth's rotation is not exact. Our perfectionist time systems must be regularly adjusted to account for nature's imperfection. (66) We try to think about the world in a linear way where the world really behaves in non-linear ways. Most events need to unfold along particular paths, something that cannot be controlled. Evolution is an unplanned process.
Within all phenomena, events and objects arise in co-dependence or as causes and conditions of each other. This can occur both linearly and cyclically according to the heuristic of dependent origination. Arising implies change, which is a continuous phenomenon. The heuristic also implies that nothing occurs in isolation as all objects and events are dependent upon other objects and events. Thus everything according to this heuristic is empty and has no inherent existence within itself. Meaning depends upon relatedness. Without relatedness there is no meaning. Thus the very paradigms we use to examine the environment lack the depth and vocabulary to explain what is taking place to others. Metaphor and analogies simplify the explanation and expression of events and phenomena which may weaken our understanding of meaning.
5. Dependent Origination and the Environment
The word environment covers vistas from the immediate social and physical manifestations of the local area to the entire cosmos. Each environment vista can be seen as a system within a system, within a system, within a system. Dependent origination infers the concept of non-permanency which runs parallel to the concepts of evolution, change, adaptation, and maybe even progress. Everything is constantly changing where no object retains all of its component parts, qualities and characteristics from one moment to the next. (67) Other than quantum mechanics, dependent origination has rarely been applied to anything else. The author postulates that dependent origination is the natural law that can be seen to govern all systems, although detail in how to apply these concepts is scant and vague and would be the subject of wide and long research. (68) At best the author can link the dependent origination heuristic with other theories and phenomenon for others to accept or reject the analogies.
6. The Gaia Hypothesis
James Lovelock, a British inventor and scientist, became interested in the atmospheric parameters on Mars when he worked with NASA on the Viking project in the 1960s. In finding that the Martian atmosphere was stable in chemical equilibrium with an abundance in carbon dioxide, where little oxygen, methane, or hydrogen existed, Lovelock hypothesized that any life would have to make use of, and thus alter the atmosphere to exist. This was in great contrast to the Earth's atmosphere which had abundant oxygen that could sustain life. (69) This contrast led Lovelock to hypothesize the Gaia hypothesis that the Earth behaves as a single self regulating system made up of physical, chemical, biological, and human components. (70)
According to the Gaia hypothesis all physical surroundings, features of the earth, pedosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere are totally interdependent and act as a single physiological system. Everything within the earth's ecosystem is of equal value and is necessary for other features to operate as systems. Every phenomenon and process is reliant and in-turn relies upon other systems and phenomenon to react upon to exist. Conditions on earth thus rely upon a physical and chemical homeostasis which is the result of interacting systems and the systems within the systems, within the systems. Consequently Gaia is an arising system that operates according to heuristics rather than linearity. Thus total predictability does not exist where phenomenon cannot be necessarily explained through mathematics. (71) The Earth 'acts' without any purposeful design, but is at the same time an emergent entity. One of the most important aspects of the Gaia hypothesis is the cybernetic feedback loops that regulate the Earth.
Lovelock mentions that although the Sun has increased luminosity by 25% since life began on earth, the earth temperature has remained the same for 3.8 billion years. (72) In response to criticism by W. Ford
Doolittle and Richard Dawkins, (73) Lovelock developed a computer simulation model which he called Daisyworld to demonstrate the Gaia phenomenon.
The principles of lovelock's Daisyworld model are not un-similar to how the human body regulates temperature. Benzinger et al. found that the human body decides upon body temperature levels through the brain making decisions based on data received through the nervous system from major organs, i.e., there is no central decision making mechanism (74) When the ambient body temperate is too hot or cold, the body responds by sweating, dilating blood vessels to regulate blood flow, shivering, and/or burning fat to produce heat.
Lovelock and Andrew Watson utilized the same approach to understand the dynamics of the earth. (75) The computer simulation of Daisyworld represents an earth like planet revolving around a Sun like star to our own. The surface temperature on the planet is affected by the colour due to the albedo effect. (76) In the case of Daisyworld is mid-toned with a moist fertile grey soil that is fertile allowing seeds to germinate above 5 c. Optimal growth occurs at 21 c but declines as it gets hotter. When the star has grown large enough to raise the surface temperature above 5s c, daisy seeds begin germinating and growing. In this initial cold stage, dark daisies are encouraged as they absorb heat and warm the surface, and light daisies discouraged as they reflect heat away and cool the surface. Therefore during this early stage dark daisies vastly outnumber the light daisies.
Over time the expanse of black daisies raises the surface temperature of the planet until it rises above the optimal growing temperature of 21 c. This encourages light daisies to grow and compete with the dark daises for space. Eventually the cooling effect of the light daisies will adversely affect surface temperatures until a steady ratio of dark to light daisies are established. The mean albedo ratio will be close to the level needed to maintain an optimal growing surface temperature for daisies. This ratio will vary seasonally as the planet is at the perigee of its orbit around the sun where light daisies will be encouraged and when the planet is at the apogee of its orbit around the sun where dark daisy growth will be encouraged.
The complexity of the model was increased with the introduction of herbivores (rabbits) and predators (foxes). (77) This only added to an improved state of homeostasis. Plagues and disasters were introduced where up to 70% of the daisy population was destroyed bringing temperature changes as a consequence. However the system showed its robustness quickly returning to previous levels of affluence. Many other layers of complexity have been added to the model showing the system to be very adaptive.
The Daisyworld model shows that biological foresight is not necessary for regulation of the Earth, which can develop "without any guiding hand of a creator". Daisyworld also shows the cyclic nature of evolution that brings emergence and transformation. The model also demonstrates coevolution or co-arising rather than the concept of "survival of the fittest" paradigm. Daisyworld is a holistic model operating along a heuristic that reductionism could not have determined, giving new perspectives about the evolution of systems.
The Gaia hypothesis offers a new way to look at the Earth as a whole without divisions into single disciplines, enabling new insights into the behavior of the biosphere, atmosphere, and physical aspects of the planet.
The Gaia model may be a better way of understanding global warming rather than considering the problem through narrow sets of variables like temperature and greenhouse gas relationships. The Gaia perspective takes into account a much larger set of variables like the atmosphere, oceans, forests, and human settlement, etc., although it may not be as predictive as single and double variable models. Thus the heuristic of dependent origination seems to superficially fit the concept of Gaia. If this is so, then this demonstrates the cyclic nature of dependent arising outside of the problem of human suffering discussed in the Dharma.
7. The Solar System
There has been a great focus on the subject of dependent origination and quantum mechanics of late, (78) but one only has to look as far as our local solar system to see the possibilities of dependent origination in action. Over the last 30 years our views have drastically changed from seeing the solar system as an empty and orderly system of planets orbiting the sun, to seeing the solar system as a dynamic environment. (79) The solar system behaves very differently to the Newtonian order (80) we once thought and is a much more chaotic, but at the same time is an interrelated and integrated environment. The actual physical properties and behavior of objects within the solar system are not so much determined by the intrinsic nature of the objects themselves, but more by their interrelationships and interconnections with other objects and dynamics within the solar system. This perspective has much more in common with the concept of dependent origination than the Newtonian view of the universe. The validity of dependent origination can best be demonstrated by looking at the formation of the solar system and the way the Earth is protected from threats by the solar system.
There are a number of hypotheses about the formation of the solar system. However observation of a number of young stars that had debris discs of dust surrounding them (81) has led to the wide acceptance of the nebular theory, originally espoused by Emanuel Swedenborg in 1734 in explaining the formation of the solar system. (82) This has since widened to apply to how the universe formed. (83)
According to estimates the solar system began forming approximately 4.6 billion years ago as a giant molecular cloud which spanned light-years across. (84) The Sun formed as a result of gravity forcing gases and debris to clump together at the centre. Based on observation of protostellar nebula in other parts of the universe, the Sun formed inside a giant molecular cloud which collapsed. This formed a small dense core gradually growing from accumulating hydrogen which eventually turns into the sun. (85) The high inner temperatures drive out all volatile materials like water and some rocks, leaving behind only the elements like iron. This was surrounded by a hot gaseous nebula that undergoes a compression due to gravity into an equatorial disk full of debris which slowly rotates around the Sun. (86) At this stage the force of gravitational collapse creates energy. Once the Sun becomes sufficiently large enough, hydrogen fusion begins. Through further collapses the clouds form rings and combine into small planetesimals of dust and ice that eventually to form the surrounding planetary system. (87) Some of the mergers of these planetesimals are extremely violent forming terrestrial planets close to the sun while in the other part of the solar system gases and ices combine to form the large gas planets. (88)
Rocky planets tend to be formed in the inner part of the gaseous disk due to gravity pulling the denser materials inwards at a faster rate than the gases. Small planetesimals quickly gather mass by collecting other rocky material on their orbit around the Sun. (89) These growing bodies tend to dominate the inner planetary system, absorbing smaller planetesimals. Once the mass of these inner plantetesimals grows large enough to disturb the orbits of other plantetesimals, orbital eccentricities occur where conditions may become chaotic. (90) At this stage collisions may occur where only a few planets may survive. Tens of planetesimals may form a single planet with an equal number being thrown out into the far parts of the planetary system. (91) Many of the planetesimals from the asteroid belt may have brought water to the earth. (92) Richard Hoover of NASA postulates that life also came to earth with a meteorite. (93)
Our observation of other solar system formations indicates that these gas planets are caused by viscous dissipation of turbulence (94) and the collection and subsequent inflow of gas into the forming planet. (95) Because these planetesimals are outside the planetary snow line and consist of ice, these bodies are able to trap gases and particles quicker and thus grow much larger than the inner planets. (96) The outer planets like Neptune and Uranus may have been in the vicinity of Jupiter and Saturn during formation, and started forming too late to collect large quantities of gas. These planets somehow drifted outwards to their present orbits over time. (97)
The ultimate transformation of nebulae into planetary disks and later planets depends upon many different factors and mechanisms. If the gas giants form too early, they may prevent the inner planets forming by negating inner planet accretion. (98) If they form late the inner planet dynamic will be more violent maybe resulting in fewer but larger inner planets, leaving a larger asteroid belt. (99) If the large gas planets are close to the inner solar system, their force of gravity may eject planetesimals from the system completely. (100) In the case of our solar system Jupiter had minimal influence upon the inner planets because of the distance from the inner solar system. (101) In addition, if the star ejects materials through bipolar jets and powerful UV radiation ejects gas from the surrounding disks, and powerful radiation ejects dust from the disks, a planetary system may fail to form leaving just a remnant disk of dust and debris without any planets. (102) After the formation of the planets many planetesimals remain in the form of asteroids spread throughout the planetary system. Comets are usually remnants of planetesimals from the far reaches of the solar system that track close to the Sun on their orbit through the planetary system.
The Earth's distance from the Sun provides ideal conditions for life as we know it. A number of situations and forces assist in preventing dangerous threats to life on life. The size of the Earth is not too small as to have inadequate gravity to prevent the atmosphere escaping and not too large where the gravity would trap a large atmosphere composed of poisonous gases to life. (103) The atmosphere itself acts as protection against most meteorites that burn up due to friction when entering the atmosphere. The Earth's magnetic field generated by the movement of molten iron inside the Earth's core protects the Earth from solar flare and cosmic radiation. (104) The ozone layer at the edge of the atmosphere protects us from UV radiation. The outer planets, particularly Jupiter acts as a trap to capture comets traveling from the Kuiper Belt in the outer solar system inwards towards the Sun, just as Jupiter did in 1994 when it captured Shoemaker-Levy 9 comet. (105) The heliosheath is a bubble of charged particles where the Sun's solar wind that meets the solar wind from intersteller space that forms a bubble of charged particles at the edge of our solar system. This forms a shield which prevents cosmic rays from outer space entering our solar system.
Just like the Gaia hypothesis, the formation of the solar system happened without the need of a creator. It is more like a process of cosmic natural selection. (106) The solar system developed through arising and cause and effect, resulting in an 'existence ' built upon karma (action and reaction). As such the solar system is a self organizing system in continual non-equilibrium. This maintains a state of change and transformation within the guidance of a heuristic rather than any predictable mathematical formula.
8. The Economic Environment
The economic environment unlike the Gaia hypothesis and the solar system is almost totally constructed through human endeavor and enterprise. (107) Although the economic environment is a human creation, it is just as complex and beyond our full understanding (108) and control. (109) According to the Nobel Prize Laureate Friedrich Hayek, any central bank would not possess the relevant information about the supply of money, nor have the ability to use that information usefully. (110) The number of recent economic crises around the world stands as testimony to that.
The economic environment is an open dynamic system that all human life and endeavor takes place within. Thus the economy is a cultural environment that operates according to our values. For example, the American dream of owning a home has greatly influenced the structure of society in the United States where the housing and mortgage markets are extremely important facets of the economy. Peoples' values are often reflected in political values that influence policy and regulation. Thus the strong belief by political leaders in the free market led to minimal regulation in many economies of the world. In other countries where it is believed the state should play a major role like China, Cuba, and Vietnam exhibit a totally different structure to those economies of the Western world. Other economies in Europe and to a certain extent in Australia reflect the values of a welfare responsibility of the state and are structured yet differently again.
The economic environment is about behavior and how it is organized. The economic system is the means by which activity is redistributed. For example U.S. and European industry has relocated to countries like China and India, changing the factors of production, market structures, organization of business, and social conditions in both the places it was relocated from and places it was relocated to. (111) The economic environment reflects power. Over the last forty years we have witnessed the transition of power from government during the Second World War, to labor in the 1960s, (112) to business in the 1980s and 90s, and to the financial sector this millennium. (113)
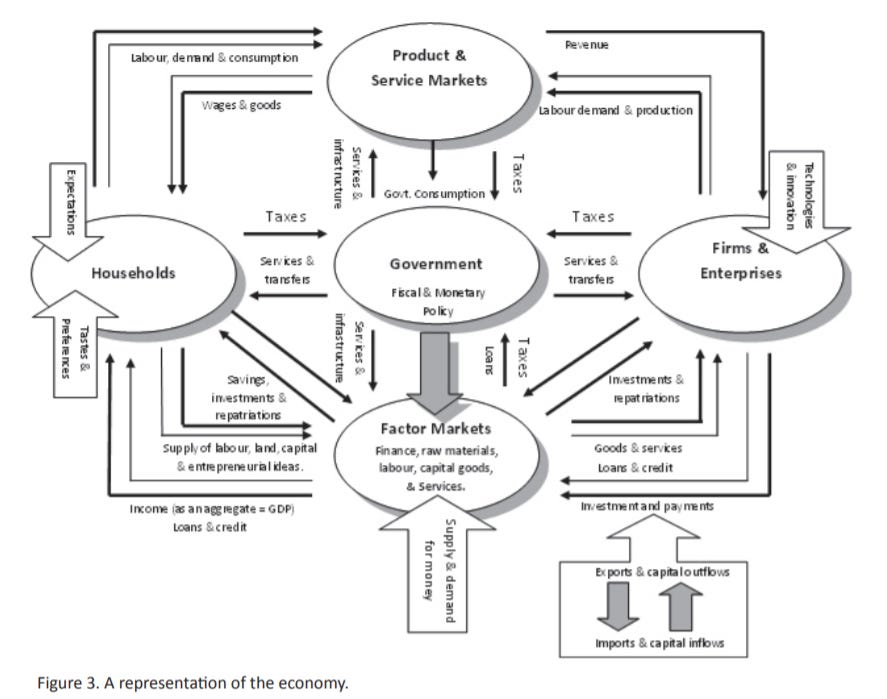
It is far beyond the scope of this paper to provide any in-depth description of the economic system. Only a scant sketch will be provided to demonstrate some of the dynamics the fit within the heuristic of dependent origination. Figure 3 represents an open economic system made up of households, firms and enterprises, government, factor and product markets, and the coupling with the overseas sector.
Households basically supply labor to firms in return for wages from which they purchase and consume goods and services. In addition to consumption, households pay taxes to government, save and make investments. Some households may directly through entrepreneurship develop some new ideas into an innovation that attracts consumption through adding some value to goods and services available in the market. In return households gain interest payments, and other repatriations such as deferred superannuation benefits from the savings and investments they make. Households also play a major role through their tastes and preferences in what is produced by firms. In a dynamic economy this is always shifting providing new opportunities in the marketplace for firms and enterprises to develop and exploit. (114) Household expectations as consumers also influence the level of activity of firms and enterprises.
Firms and enterprises produce products and services for households. They also produce for other firms and purchase goods and services from other firms through factor markets. Demand from households and other firms determine what a firm will produce in an open economy. Firms and enterprises also borrow and take equity through factor markets and make repayments on loans and repatriate profits through factor markets. Firms and enterprises pay taxes to government and receive services, infrastructure and subsidies back from government. A firm's ability and capability to produce is subject to the access to technology.
Two types of markets exist in any economy. Product and service markets provide products and services to households, other firms and government. What and how much to produce is directly influenced by demand in these markets. The level of demand will directly influence the level of economic activity. Taxes are collected by government and the government is also a consumer, supplies infrastructure and regulates the markets. Factor markets are basically markets where firms and enterprises acquire raw materials, capital goods, finance, and equity for maintaining operations. Households also supply labor through factor markets (traditionally organized through trade unions). Entrepreneurial skills can also be seen as a factor of production that differentiates products and services from other product and services, explaining diversity in this simple model.
The government plays multiple roles in the economy. The government is a major consumer of goods and services and the level of government consumption has great influence on the overall level of economic activity, i.e., high consumption stimulates demand and low consumption dampens demand. The government also supplies infrastructure which assists economic activity and national competitiveness. Through the provision of infrastructure, government's can stimulate employment and demand through what is called the multiplier effect. (115) Through taxation, governments also regulate demand, i.e., lower taxes may lead to more consumption or saving), higher taxes may lead to less consumption or less savings). Government can also regulate the economy through monetary policy where money supply and interest rates are regulated. This is usually undertaken by a statutory body like a central bank that makes decisions free from the influence of the executive government. Through setting relatively high interest rates, the demand for loans and finance will be generally dampened leading to lower levels of economic activity. However high interest rates may attract capital inflows which that put upward pressure on currency exchange rates, making exports less competitive and imports relatively cheaper than local goods. Lower relative interest rates may encourage more lending and boost demand, however capital inflow may decline due to better potential returns in other economies, putting downward pressure on exchange rates, but making exports more competitive and imports more expensive. Lowering interest rates at a time of high economic activity may raise the rate of inflation.
The economy is linked to the rest of the world through exports, imports and capital inflows and outflows. As discussed above the currency exchange rate directly affects the competitiveness of exports internationally and price of imported goods in the domestic market. Capital inflows and outflows almost always directly affect the value of the currency. Central banks usually purchase local currency overseas when the exchange rate is under downward pressure to maintain currency value levels. However prolonged use of this method to maintain stable currency rates will drain a country's international reserves which are needed to finance the purchase of imports.
In this very simplistic view of an economy we are able to see that it is totally integrated and interrelated where each sector is co-dependent. One event or action will give rise to other events or actions in complex ways that are not easily easy to foresee. For example, changing exchange rates can potentially produce many different possible actions within the economy, but the end effect will depend upon a number of variables acting together, e.g., the exchange rate may be influenced by overseas demand, capital inflow, the level of imports, the level of exports, and interest rates, etc. Foreseeing potentialities would prove more difficult when one takes a reductionist view of the economy. There are no algorithms that can predict outcomes. The economy is a total system where looking at only one of the parts will not lead to a full understanding of what is actually happening.
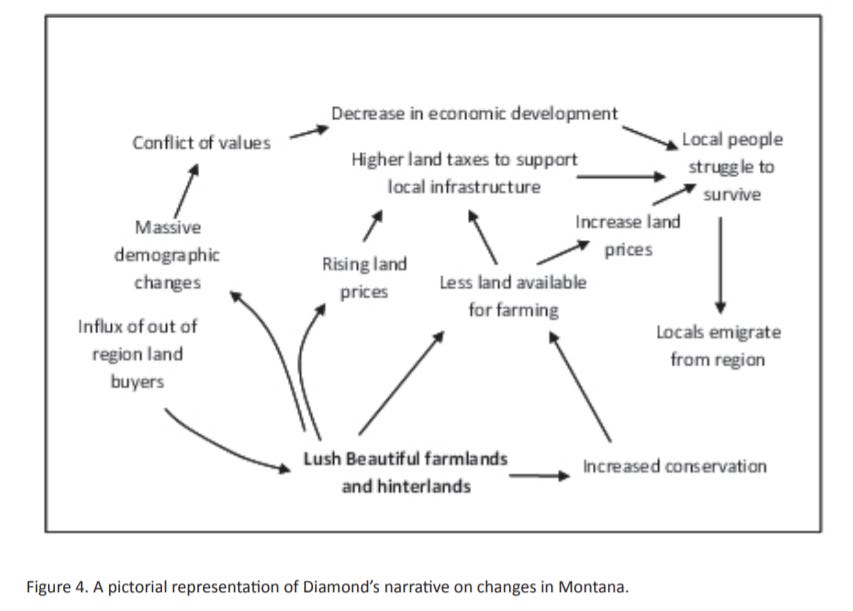
Jared Diamond in his book Collapse looked at the cause and effect of conservation and the influx of retirees to Montana. (116) Diamond described how the beautiful scenery of the Montana plains attracted retiree settlers who wanted to maintain the pristine scenery through conservation. This lead to less land being available for farming and drove up land prices and taxation, which made it very difficult for locals to make a living through farming. The demographic changes occurring through new retirees settling in Montana led to community conflicts. Overall increased conservation led to lower economic activity where locals struggled to survive, and eventually many locals had to emigrate from Montana to find new livelihoods elsewhere.
9. The Social Environment
The concept of dependent origination provides a structure by which we can observe social phenomenon. Dependent origination highlights duality within the social environment and is particularly useful for looking at how attitudes, values, beliefs, and assumptions evolve within society. Although the concept of dependent origination was applied to individuals by Siddhartha Gautama, some sutras mentioned social issues. (117) Through a collective consciousness a mechanism that culture provides, dependent origination can be extended to the social level. (118)
Our perceptions of others in society are relational and dependent upon other entities. Therefore the thoughts, emotions, desires, and the activities of others affect our perceptions. Our personal desires can be considered to be based on the 'relational gap' between the observer and the observed. (119) Consequently events in society can be deemed to be co-arising, i.e., one group's aspirations arise in relation to another group's actions, needs, wants, and desires. Our personalities, motivations, realities, and behavior are all connected to society through relatedness. We tend to act and behave according to our social identity, be that a parent, lover, husband, wife, child, teacher, engineer, or doctor, etc. The identities we exist within can be both a resource and a psychic prison in our outlook. (120) Our identities also exist within a semiosphere where all consciousness and mention projections are exhibited and reflected in the symbols, artifacts, and language created by society, reinforcing communication, behavior and our state of relations between people. (121)
All our actions that we undertake take place within a society which is a field. This field is where individuals interrelate and become a conditioned product of the field. However, the field is also a product of our combined social actions. As our life develops in the field we become socially conditioned. We become embedded with ideas, needs, wants, desires, and aspirations. The whole society is built upon desire. We compete for grades at school, for our mates, in our career, and for social status. Our economic and political system is built upon desire, where we become delusional through believing desire is happiness. This state brings ignorance to the true nature of life where we become stressed and develop all sorts of anxieties and defense mechanisms to suppress these truths, where we may develop psychic behaviors like paranoia, obsessive-compulsiveness, become attention seeking, depressive, schizoid, or narcissistic. Which bring dysfunctional behavior both at the individual and institutional level. (122) We are a free agent but act according to our 'contrived self' bounded by ignorance, clinging, and craving to what provides us with a sense of security and pleasure in life. Thus the 'contrived self' has an ethical view of self interest and may practice all sorts of strategies to maintain their position in society.
Humans are well equipped to promote their self interests through their empathetic processes that can manipulate others. Recent studies on narcissistic individuals has shown that there are two types of empathy, affective empathy and cognitive empathy which involves the ability of people to see person's emotional state without being able to feel what they are feeling. (123) Lack of empathy can also be compensated by strategizing and spontaneous mentalizing to manipulate others to their advantage. These "Machiavellian" personalities don't necessarily feel the same emotions as those with empathy receive, so don't feel guilty when manipulating others. (124) This type of behavior can be seen in short-term mating strategies by males. (125) Political interactions are perpetuated by our Machiavellian mind. When considered through the dualistic nature that dependent origination predicts, one can consider political movements as phenomena arising and co-arising in reaction to other phenomena. Throughout history, the proletariat has arisen when feudal or industrialist existed, the educated professional had arisen when royalty rules, labor had arisen when the conservatives ruled, and fascism had arisen when communism existed. The view that power generates resistance popularized by Paul-Michel Foucault is supported by the dependent origination heuristic. (126) Events like the First and Second World Wars, the Vietnam War, Iraq, and the rise of radical Islam may be interpreted through existence and arising.
Society is created through a latent karmic imprint which formed the culture, language, customs, economy, technology, and everything else around. This imprint is the karmic potential of where society can progress and evolve to. This concept of karmic imprint could be equated to Bourdieu's concept of capital, of which four types of capital exist: Economic capital the level of financial resources, buildings, technology, and plant and equipment, etc.; Cultural capital--knowledge based on a shared history which equips the social agent with empathy toward for, or appreciation for, or competence working within the cultural rules and norms within the field; Social capital--consisting of resources obtainable through connections and group networks; and Symbolic capital--which include socially derived symbols like university degrees, or acceptance by social institutions within the field. (127) Capital is a major determinant of the capacity to exercise influence over the field and thus control our own future. (128)
10. Event Phenomena and Entrepreneurial Opportunity
How entrepreneurial opportunity arises has never been fully explained. We can explain in detail how to go to the moon, land on it, walk around the surface and return safely but we cannot satisfactorily explain how people find opportunities. There is no generally accepted theory about how people see, discover or construct opportunities. It is still very much the unopened black box of entrepreneurial activity, (129) yet to be fully understood. To date it has only been explained by anecdotes and fragmented approaches. (130)
Dependent origination may be able to offer some perspective. Part of our Newtonian view of the world considers all events external to ourselves where we are just an observer. However the way that dependent origination has been expressed through the Dharma postulates the perspective of inputational or imagining nature where all independent entities in everyday life are ultimately illusionary. The physicist and philosopher Bernard d'Espagnat uses the example of a rainbow to describe the classical illusionary view of the world. A rainbow is not an object in itself, it is an illusion that we observe with the sun and raindrops there as a prerequisite. As we move the rainbow also moves and our view of the rainbow depends exclusively on our position. Thus the rainbow only exists because we are looking at it. The rainbow is a sensory imputation, a phenomenon not independent of our selves. (131)
Reality exists because we are aware of it. If we extend this view of reality, then our observations also have a creative impact on history, where not a single history exists, but rather multiple histories representing multiple realities. (132) The universe may just be one giant cosmic dream shared by all the world's inhabitants. (133) No phenomenon is a phenomenon until we observe it. (134) Thus the universe exists because we are aware of it, (135) and entrepreneurial opportunities exist because we are aware of them. Opportunities are not independent within the environment, they depend upon a person to give them structure and character.
Entrepreneurial opportunity is about how we interpret reality. Any history or event can have a number of interpretations, (136) all of which may contribute to our knowledge. (137) If we accept the concept of multiple histories through multiple interpretations, any of these interpretations can be projected into a kind of possibility, a future potential that can be actualized, which requires our personal sentiment to perceive, experience and project. Thus as Henry Stapp postulates, the connection between the physical and our knowledge is two-way, where knowledge is created through the selection made of what interpretation we desire. (138) Therefore as an observer- participant in the environment looking at all the vast array of potentialities, our perceptions of possibilities drift both backward and forward in time. Opportunity becomes a mix of what Bohm calls the "implicate order" and the actualized experience of the "explicate order ' of the world, which becomes our reality. In this way what we implicate becomes explicate over time. (139) In terms of entrepreneurial opportunity, rather than passively observing reality, we in fact make our own realities.
It is our own awareness that materializes the physical world enabling us to see potential futures. The process of opportunity recognition is not dualistic as the person through their curiosity and attention has become involved with the environment. Our division between ourselves and the environment is a matter of social construction. It's about our relatedness with the environment of which we 'empathize ' through the view of our own self efficacy with the skills, competencies, capabilities, resources, and networks we have available at their disposal. We cannot be separated from the environment because when we are developing new business models and strategies we are already part of the environment. Therefore metaphorically through creating different opportunity scenarios, we are creating potential parallel universes. These become the narratives which enable different meanings.
What determines new opportunities is not seeing what others do, but seeing what others are not doing. Opportunities can come from various insights where; one can see improvements for existing products, new resources that can be made use of, new materials that can be made use of, new processes that can be made use of, possibilities for new products, possibilities for new ways of doing things, new ways to get a product to customers, new customers, technologies that can be used for different applications, and technologies that can produce existing products more efficiently and/or superiorly and even create new industries. Without curiosity our observations become lazy and complacent, and we only observe the familiar with what we have had a long association with.
Generally it is explained that opportunity gaps arise out of environmental change, driven by changes in the social, economic and technology conditions. (140) Government and regulation also create opportunity gaps through the allowance of certain things and the disallowance of others. Consequently changing laws and regulations are another source of product opportunities. (141) These are the environmental factors that together drive product, market and industry evolution. When a person looks at the environment there is a complex number of factors that need to be perceived and understood for meaning to occur. Each individual factor has a meaning and together with other objects creates complex field of inter-meanings. Any environment has the following factors:
a field,
objects within the field,
relationships between objects, actors,
relationships between actors, events,
relationships between events,
relationships between actors and events,
relationships between actors and objects,
relationships between actors, objects and the field,
relationships (or no relationships) between everything,
the situation,
movements and stillness, motives,
relationship between self and the actors,
objects and the field,
and interpretations of the above.
The environment can be seen in terms of the above factors to better understand their dynamics and inertia. There is the potential to discover connections between the various field elements. Where one can see interrelationships and trends, where movements and opportunities can be discovered and constructed. However when we are immersed within the system itself, it is hard to see the dynamism of the elements of the field and we act in a similar manner to others as we cannot see any change. (142) Our existing knowledge can constrain and keep us within our existing bounds of thought. It is only when a person can be aware of their own biases or mental models that they can see and think beyond it. When one is free of existing thought patterns, new connections between unrelated actors, objects, events and the field can be seen. Through imagination new potential realities can be formed internally leading to change in the existing mental models. This is the point where creativity flows and innovation may occur.
From the dependent origination perspective, any phenomenon will only arise in relation to another phenomenon, where everything is mutually dependent for existence. Therefore new opportunities are "latent karmic imprints" i.e., seeing the latent potentiality that exists for some new reality, that observer-participants perceive in order to trigger the creative action necessary to construct or discover new opportunities. All notions of causality and effectuality are actually manifestations of the mind rather than something out in the environment.
It is what exists in the past and present that guides what can exist in the future, as it is the past and the present that sow the seeds of potentiality for something in the future. Thus the future is guided by the karma (cause and effect) that has taken place to provide the range of possibilities. Thus for any opportunity to actually exist, it must be realizable. For example, the difference between Jules Verne's fantasy of man landing on the moon and the Apollo 11 moon landing is not vision, but available knowledge and technology, and a sense of national will and endeavor to achieve the goal. We are all dependent upon what has gone on before and the present to have specific potentialities. In this way our emergence is path dependent but not totally predictable.
We are also locked into the past through the grounding of knowledge we have. If we see all the past actions, events, knowledge, and experiences as something similar to Jungian archetypes, we are bound to repeat the past through using and mixing these archetypes repeatedly. (143) It is a unique mix of existing archetypes that creates innovation. Thus innovation is something bound to the past. The environment may be different but the behavior will be the same according to the archetypes we know. Opportunities are emergent from the realms of archetypes of the past, thus bringing the environment into endless cycles of repetition based on past knowledge and experience. Our emergence and evolution is thus cyclic according to the principle of dependent origination.
11. Consciousness and Self Concept
A person's perception continually ebbs and flows on a daily basis with changes in intelligence, knowledge and understanding, based on the type of emotions one feels and their individual strength, pull and intensity. This process makes a person happy, sad, excited, hesitant or anxious about people, objects and events around them. One may feel angry, greedy, jealous, trusting, lustful, and confused all in one day. More often than not, we are not aware of the influence of our feelings upon how we perceive things and behave, as this process is partly sub-conscious. (144) Feeling is what drives a person, whether it is to seek shelter and food, clothing and medical care, love and sex, career and comfort, etc. According to Buddhist Dharma (theology), desire is a major part of our motivation and psych.
Within the Abhidhamma Pitaka, the last of three parts to the Pali Cannon (the scriptures of Theravada Buddhism) are a number of texts concerning psychology, philosophy and metaphysics. The Abhidhamma Pitaka describes the structure of the human mind and perception with amazing accuracy to the accepted views of modern neuroscience. The mind is described as a continual conscious process or experience in the metaphor of a 'mindstream ' (something similar to phenomenological psychology). (145) Buddhism sees mankind living in a deluded reality caused by infatuation, attachment (146) and clinging to desire for objects and permanence in the world as the source of all suffering. The pathway to wisdom (147) is found through understanding 'The Four Noble Truths ' (148) and practice of the 'Eightfold Path. ' (149) Many of these practices are being used in modified forms for therapy today. (150)
Buddhist philosophy combines both consciousness and metaphysics in the concept of Pratityasamutpada or dependent origination. Reality is seen as an interdependent timeless universe of interrelated cause and effect. A human's existence is interwoven with the existence of everything else and the existence of everything else is interwoven with the human's existence in a mutually interdependent way. Because this concept is past, present and future, everything in the universe is only transient and has no real individual existence. This is a very important concept because it is only our ability to free ourselves from attachment and delusion about our sense of self and values unconsciously placed on others, will we be able to see the world as it really is, rather than what we wish it to be. In fact our view of self and existence is created through our clinging and craving which blinds us to the reality of dependent origination. As we have seen, Buddhism is about transcending these delusions so human perception is clear and unbiased. This makes Buddhism an ethical philosophy of life, rather than a religion in strict terms. (151)
Since the beginning of the Twentieth Century, especially after World War II, there has been a growing interest in Eastern philosophy in the West. The teachings of the Abhidhamma Pitaka have inspired and influenced many psychoanalysts and psychologists, (152) including Carl Jung, Erich Fromm, Albert Ellis, Jon Kabat-Zinn and Marsha M. Linehan. There has been a great leap forward in humanitarian and transpersonal philosophical influence both in therapy and management theories. (153) Dialogue between philosophy theorists and practitioners of East and West has led to mutually influential relationships between them. (154) This has led to new insights into therapies and new schools of thought on both sides. (155) Aspects of Buddhist Dharma are also incorporated in the works of Western philosophers including Caroline A. F. Rhys David and Alan Watts.
Buddhist doctrine of dependent origination pre-empted some of the most recent developments in neuro and cognitive psychology particularly in the way we experience ourselves and the affective processes behind how we create our self identity. (156) Dependent origination explains the forming of our personality, motivations, likes and dislikes, patterning and biases. Dependent origination answers the questions "what do we really want?", "why do we want such things?", and "why do we act the way we do?"
None of our wants are actually our own. Our wants and behavior are conditioned within us from our upbringing by parents, schooling, religious upbringing, and exposure to society in general. Our actions come from within the bounds of our socialization and the choices we make are decisions based upon the stream of conditions surrounding us. Our self identity is made up of the sum of influences around us. A person is the result of feelings, thoughts, and emotions, both inherited and as the result of social factors. These states develop our biases, opinions, likes and dislikes, views, and knowledge, and thus we don't really have any true self identity. Consequently our self is really a delusion which we interpret as our desires and intentions based on our ignorance of "I" and "me "--a stream of physical and mental phenomena, constantly arising and ceasing, taking influence over our mind in a constant state of flux and change. Our clinging to the identity of "I" and "me" is our greatest defense mechanism we have to cope with change, and this is the basis of our self delusion.
At this point of the discussion it is important to mention that the concept of cosmic consciousness which is sometimes described as a collective consciousness that exists throughout the cosmos and often associated with Buddhism. Cosmic consciousness has been argued as a state that can be reached through the practice of meditation. (157) Jung described connection of all nature through the 'collective unconscious'. Jung likens the external world to one of illusion, something similar to the world of Maya in Hindu theology. (158) Our egos (jivatman) are individual souls which are actually extensions of the one and only Atman, universal energy or God who allows an independent identity to manifest itself in part of himself. Through this we are all connected, independent, but interdependent. When we die we realize the illusion that we actually existed as we are part of God.
However the concept of dependent origination has no esoteric connections. (159) Dependent origination postulates that we have a common socialization through our culture, family and professional life and socialization with others which cultivates our biases, desires, values, beliefs, and assumptions. There is no known transcendent consciousness, only metaphorically through socialization and genetic inheritance. Our identity is related to the world around us, to others through identity paradoxes like rich-poor, have-have not, high status-low status, lucky-unlucky, and winner-loser, etc. People pursue their daily lives from the framework of their meaning system. We live in a structured world. Our reliance on value systems has more in common with Bourdieu's field and habitus theory than cosmic consciousness. (160) We are guided through cultural and social logic and our subjective experiences, not by causality but by co-arising, (161) which makes behavior less predictable. Daily events we participate in and observe don't rely upon the laws of physics however they are predictable enough to have rule of thumb predictions to guide daily life. The human psych is the result of millions of repetitions of thoughts and acts. A person is not really made, he or she becomes and is still becoming, predetermined by his or her own choice, thought, and act, which becomes habit. People don't always move towards a single goal or objective, they continually change direction. This is the effect of emotions.
Consciousness is a process that emerges from the interactions within our brain, body and environment; a multidimensional process with a rich variety of properties. Consciousness is thus changeable, related to interaction with people, objects and the environment, reflects our moods and feelings, and is both situational (where we are in the world), and phenomenological (about what we experience)}62 Our emotions are part of our consciousness and also our window and connection to the world. All our experiences are subjective therefore entities have a subjective existence that is ambiguous. Consciousness is thus a phenomenological arising due to mutually dependent activities and without arising conditions there is no consciousness.
According to the teachings of dependent origination it is the ability of the brain to categorize what we perceive in the environment that gives meaning. Without the ability to categorize, we would have no cultural or social realities. And it is the very system of categorization the brain utilizes that gives arise to our desires, wants, and cravings. The paradox here is that our perceptions via our emotions are actually non-existent but imaginary however through imagination they exist. This is consistent with Benjamin Hoff's concept of the social construction of identity, relying on our mental maps and stereotyping of people, objects, and events to provide meaning: "A man noticed that his axe was missing. Then he saw his neighbor's son pass by. The boy looked like the evil while he walked and behaved like a thief. Later that day the man found the axe where he left it before. The next day the neighbor's boy walked past and walked like a well behaved and good boy." (163)
When we perceive something our cognitive system identifies it and our emotional system gives it value. Thus the way one interprets the world will be the way one acts in the world. Humans act towards people, objects and events based on meanings they assign to people, objects and events. Our social interactions are based on conditioned responses based on our beliefs and assumptions. Meaning arises through the interpretation of social actions that we encounter. Therefore no absolute meaning exists--it is negotiated through interaction with others and perception of events modeled by our thought processes. (164) Our reality is based on social interaction.
Buddha's parable of a king who invited a group of blind men to identify an elephant shows that our understanding is based on perspective. One feels the tail and says it is a rope. Another grabs the leg and says it is a pillar. Another feels the side and says it's a wall. Another felt the head and said it was a water jug, and so on. We try and understand the world through the narrow perspectives we have. This leads to our ignorance and habitual behavior that uses up all our attention and energy. Only when one can transcend the influence of their ego is one able to see the through the influence of their emotions. (165)
Click on subscribe so articles can be directly emailed to your inbox: